1. VTM
1.1 VVC procedure
According to [1]:
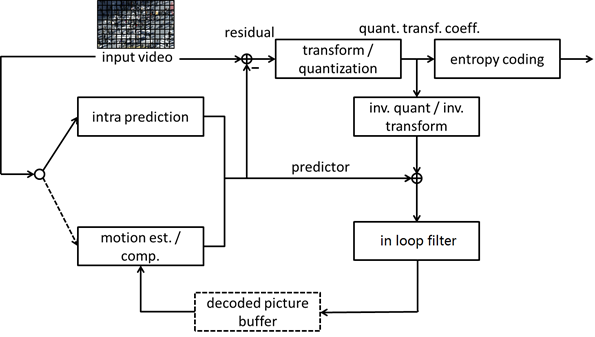
motion prediction ,transform/quantization and the optimization of entropy coding. Also, loop filter plays an important role here, according to [3], the effect of Adaptive Loop Filter (ALF) is quite obvious.In 4 basic mode that VTM provided (All intra(AI), randomly access(RA), low delay B-frame(LD), low delay P-frame(LDP)).The all-intra one do not have motion predictor but intra predictor only. According to [3] , AI,RA,and LD is asked in tool evaluation. And in the attachment table of [3], RA mode is is used for summary. Thus, the experiments next will run at RA first.
.1.2. VTM Standard configuration
.1.2.1. Goal and Prediction
To run with default configuration , we can check if VTM works functionally, and get to know how much time it will take, and the differences between these modes. Technically I-frame only will be the fastest one, because it does not need to generate motion predictor, other modes’ speeds are depend on specific GOP structure.([3])
.1.2.2. Configuration
Source Video: Campfire_320x240_10bit_420.yuv
Framerate: 10
Frame To Encode: 30
Resolution: 320x240
Depth:10bit
Config file: Default.
.1.2.3. Test 1 - RA
Total Frames | Bitrate Y-PSNR U-PSNR V-PSNR YUV-PSNR 30 a 299.6933 30.1197 29.9015 29.7325 29.8497 Total Time: 16428.927 sec. [user] 16428.927 sec. [elapsed]
.1.2.4. Test 2 - LDB
Total Frames | Bitrate Y-PSNR U-PSNR V-PSNR YUV-PSNR
30 a 28.2827 36.0232 42.3287 37.5540 36.6602
Total Time: 4385.215 sec. [user] 4385.214 sec. [elapsed]
.1.2.5. Conclusion
According to [2], a evaluation procedure asks a complete encode-decode results, with time and PSNR info. Since the evaluation table of Term project –VVC does not mark the LD mode as M and time is limited, so I will only test AI and RA mode below. Also I will adjust QP to decrease running time. According to JVET-N1010, we should use 22,27,32,37 to test.
2. PART II: VVC tool
2.1 Overview
Noticed that we can design improved method into the six main module of VVC procedure (see diagram 1). And basically all proposal about enhancement tools are based on these module. I picked ISP [4] as our to-run experiments, since it has been accepted in VTM 7 [0] , so there’s a easy way to enable it by adding parameters. And also I took a look at CST [8] , which is not accepted yet. The author of CST provided their algorithm with corresponding codes at [10].
2.2 Intra sub-partitioning (ISP)
ISP is the latest version of LIP, whose main thought was re-designed in HEVC. ISP is a improvement tool in module intra-prediction of figure 1.
2.2.1 Line-Based Intra (LIP)
2.2.1.1 LIP at Meeting K and HEVC
ISP is based on LIP, whose purpose is in meeting K, [11]. The main thought is to use intra motion predictor to decrease the size of encoded file.
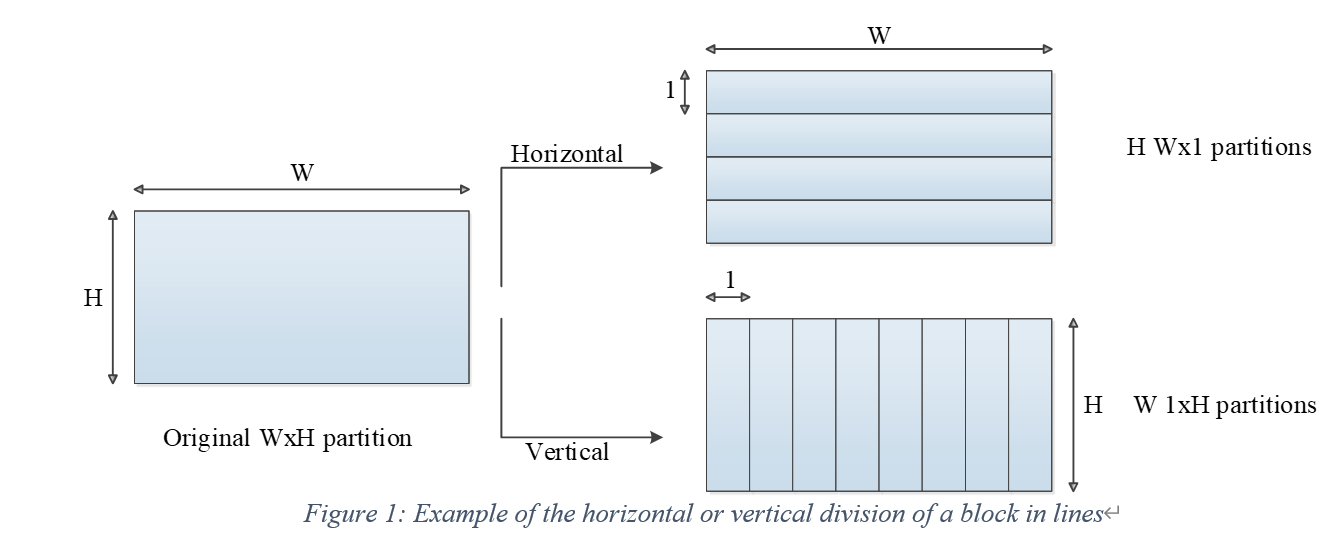
In[11], the authors provided an approach to use a horizontal or vertical to make partitions at these blocks, like figure 3 below.

2.2.1.2 LIP in meeting L
Due to high complexity, meeting L held many conversation about the tradeoff between complexity and performance. Also there are many evaluation ([13],[14]), which shows that thought LIP has a good effect on encoding, but the memory access cost is high. Especially the number of pixels may be less than 16 in a single partitions. Thus the strategy after meeting L is :
| Block Size | Number of Sub-Partitions |
|---|---|
| 4×4 | No partition |
| 4×8 and 8×4 | 2 |
| All other cases | 4 |
2.2.2 Overview of ISP
LIP is changed into ISP after meeting L.
2.2.2.1 ISP in meeting M
The strategy after meeting M is:
| lock size | Coefficient group size |
|---|---|
| 1×N,N≥16 | 1×16 |
| N×1,N≥16 | 16×1 |
| 2×N,N≥8 | 2×8 |
| N×2,N≥8 | 8×2 |
| All other possible M×N cases | 4×4 |
2.2.2.2 ISP in meeting N
Notice that from [4], which set a limitation: the ISP coding has 64x64 CUs at most. Specific CU size is:
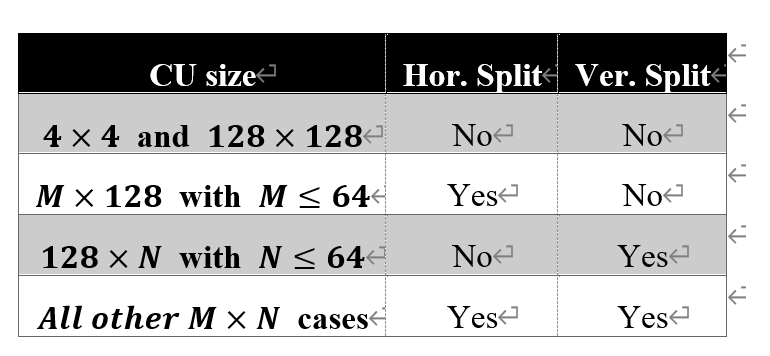
.2.2.2.3. ISP in meeting O
According to [5] ,the number of partitions is fixed for 8xN blocks, which is the the latest update in the meeting in July, 2019:
“ For 4xN coding blocks and 8xN coding blocks (N > 4) that are coded using ISP with vertical split, the prediction region is specified to be of size 4xN. ”
Besides, [6] provided a filter approach with optionally Cubic or Gaussian fliter, depends on the size of block. According to the VTM result in [6], the quality loss is controled within 0.05% in average.
[7] also provided some adjustment :
This contribution removes the MPM only and PDPC restrictions and applies always the cubic filter on CUs using ISP.
2.2.3 Conclusion
In my opinion, ISP is a series of methods deployed in intra prediction. First it checks all possible reference lines, even some far reference lines to generate possible motion vectors within intra prediction blocks. And then some advance approaches may be involved , like WAIP and PDPC([16]), which help to construct more precise blocks for objects. Then, the developers of ISP system are trying to find the best strategy to make partition and limit the maximum CU for entropy coding next. According to the knowledge of Information theory, we are actually finding the minimum quantification to get the best rate of coding. Besides, recent proposals are trying to use different partition form, which need lots of testing and evaluation.
Modern features of video ,like the shape of objects inside is usually rectangle, is playing a important role in the design ISP. I noticed that the shape of partition is rather horizontal or vertical for this reason, and we already use such thoughts in current video code. Based on the main purpose of VVC——high and extremely high resolution, we do need more partition in intra coding, and I think the main effect in these high resolution videos is come from inter-frame prediction. It is more possible to construct precise vector between frames, since we can use lots of information here, which is helpful to find suitable codebook.[19]
At last, I think we can use different partition strategy which depends on the specific resolution. Although current approaches already have such feature: if the resolution is too low, then the size of calculated partition will be too low, then according to strategy table(table 1 and table 2 above), these partition will not be made. And I think maybe we can directly set the stategy for corresponding resolution. But everything here is just a “guess”.
3. PART III: Tool Test
3.1. VTM settings
According to [0], since ISP is accepted into VTM, we can change it by adding parameters.
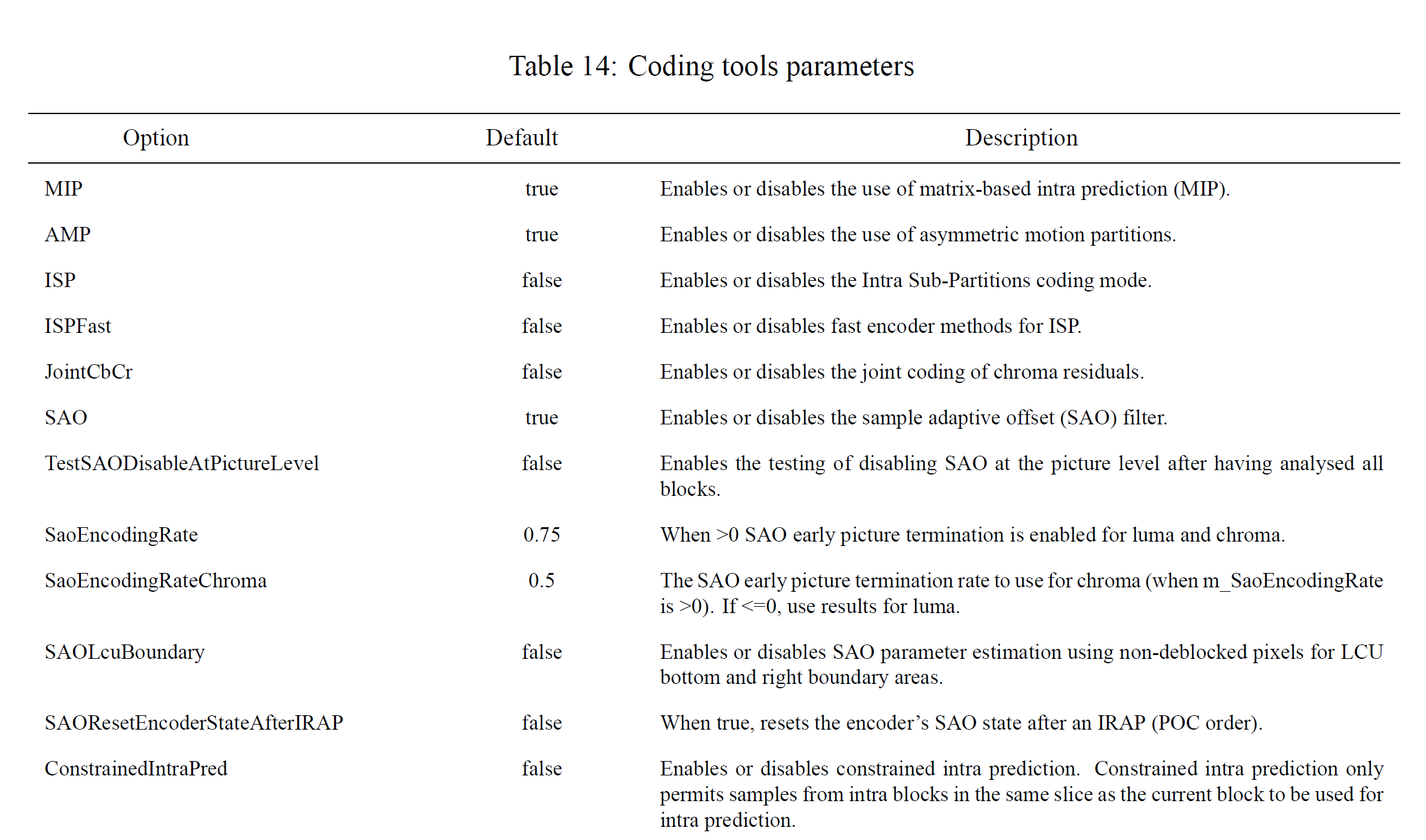
3.2. Stage 1
Stage 1 is to use both 甲 and 乙 for A1 video, and to run RA32 and AI37 (the numbers mean QP) tentatively.
3.2.1. Configuration
Source Video: Campfire_320x240_10bit_420.yuv,FoodMarket4_320x240_10bit_420.yuv,Tango_320x240_10bit_420.yuv
Framerate: 30
Frame To Encode: 30
Resolution: 320x240
Depth:10bit
Config file: Reference(ISP enabled) , Test(ISP disabled)
3.2.2. Result
3.2.2.1. RA-32
sequence: Campfire, FoodMarket4,Tango
| ISP:ON | ISP:OFF | |
|---|---|---|
| Encode time | 7416.567|2269.858|1885.974 | 4864.291|2084.174|1780.175 |
| Bit rate | 81.9840|37.0880|25.6400 | 81.3440|36.9280|25.6400 |
| Y-PSNR | 36.0677|43.1627|39.3115 | 36.0178|43.1390|39.2793 |
| U-PSNR | 42.7716|48.1737|47.7016 | 42.5136|48.2491|47.7944 |
| V-PSNR | 37.6644|47.9257|44.9709 | 37.7266|47.9088|44.8995 |
| YUV-PSNR | 36.7207|44.0769|40.5801 | 36.6778|44.0630|40.5482 |
| Decode time | 3.206|1.785|1.217 | 2.386|1.846|1.327 |
3.2.2.2. AI-37
| ISP:ON | ISP:OFF | |
|---|---|---|
| Encode time | 196.941|34.397|57.976 | 161.614|32.129|53.507 |
| Bit rate | 14.8275|8.3925|8.4675 | 14.6475|8.3625|8.2800 |
| Y-PSNR | 36.2916|44.1327|39.5017 | 36.2669|44.1254|39.4729 |
| U-PSNR | 41.4474|48.0814|46.6614 | 41.5606|47.9431|46.9379 |
| V-PSNR | 37.3301|48.7423|44.6119 | 37.2647|48.7115|44.6308 |
| YUV-PSNR | 36.8414|45.1020|40.7198 | 36.8202|45.0815|40.7096 |
| Decode time | 0.549|0.463|0.499 | 0.591|0.425|0.511 |
3.3. Stage 2
According to JVET-N1010, we should run a full test on A1 class with 4 kinds of QP values.
The result is here :
(Because I have no more time , RA22 isn’t finished)
3.3.1. Result
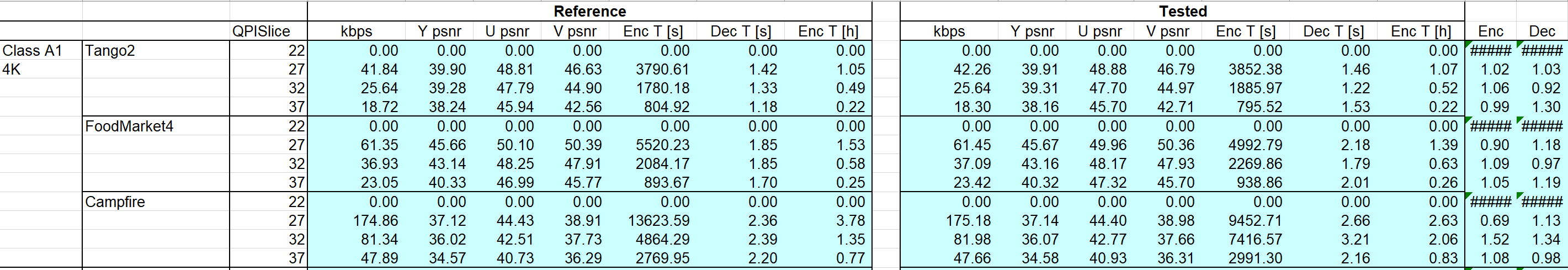
All the data can be found in evaluation excel file. Here are some screenshots.
3.3.1.1. RA,10bit
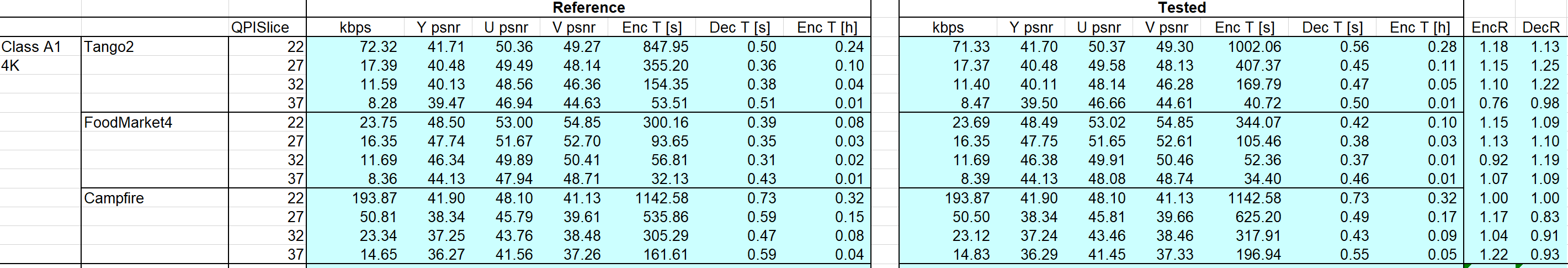
3.3.1.2. AI,10bit
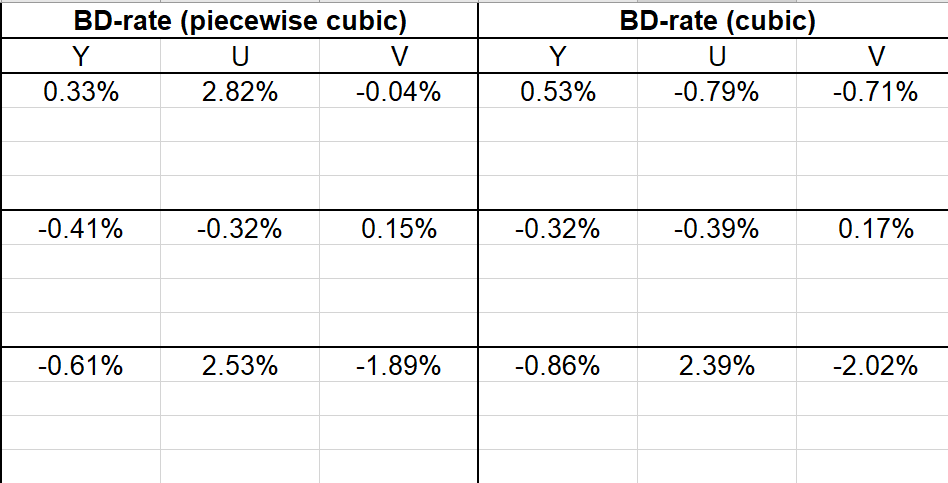
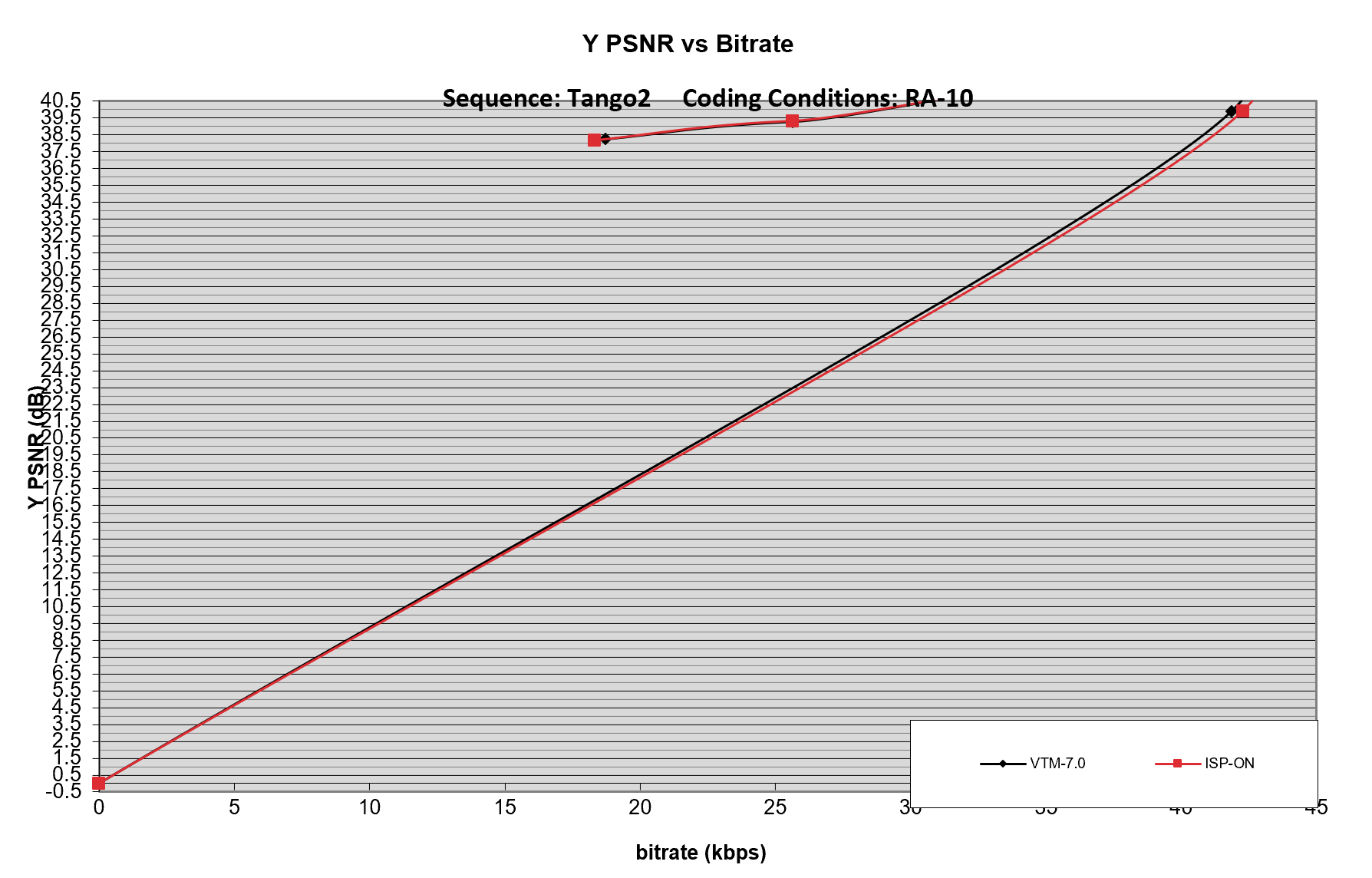
3.4. Conclusion
The reference of experiences of evaluation is [3]:
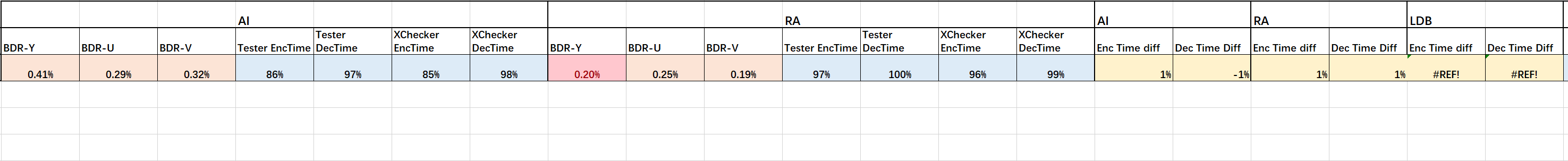
The main difference is the encoding time. I speculate that the reason is the resolution in my test is much lower than 4K, which may result in low efficiency when using ISP——the number of intra vector is fewer than standard testing, which decreases the effect of ISP. And in this case, the time cost of generate ISP for frames will be correspondingly high, while the partition operation is hard to implement at this resolution. Besides,ISP tool have to decide and construct partition marks in procedure. Additionally, since some other tools are enabled by default, so there may exists some coeffect to influent encode efficiency.
As for unsteady PSNR , I speculate that the reason is our cut method is like a “zoom-in” for source 4k video. This will result in blur and much lower inside information, and a much important point is that there will be more “jump in” objects in low-resolution video, and that is why the result between different video varies.
Technically, since ISP use partitions for each block with size limitation, it may can’t work fine at this resolution and this type of video. And we can see that in fig. 10, there’s a little negative gap, which means ISP results in worse quality in same bitrate, which means ISP does help compressing.(Same quality, lower bitrate) ( I don’t know what the wired reentry curve at the top is)
At last, a general phenomenon is the lower the QP is, the more “complex” the binary code will be. “Complex” here means longer encoder/decode time, higher bitrate, and higher PSNR. A few records of encode/decode times do not follow this rule. I think the reason is that they are from stage 1 of this experiments. So my computer’s condition is different compared with stage 2, for I was running other program. CPU scheduling will not always be same.
.3.5. Future Improvements
- I should use
batto run lots of the decode/encode automatically, which will increase efficiency, and create more data about this experiment, which will be positive for analysis and conclusion. - Coeffect between tool may exists.
- As for condition 甲 and 乙, I think the better way may be make scaling at first, then cut. This approach may bring more details in videos. Current videos is blurred and contain few objects in detail. And few rectangle object is inside. So ISP’s feature may can’t exert very well.
4. Reference
VVC and VTM documents:
[0] Soft-manual of VTM 7.0
- [1] JVET-P2002-V1 Algorithm description of JVM
[2] JVET-P2011-V1 Test and evaluation procedure of JVM
[3] JVET-P0013-V1 Tools of VVC
Tool documents of ISP(Assigned by P0013):
[4] JVET-N0308-V2 Restriction of the maximum CU size for ISP to 64×64
[5] JVET-O0106-V2 On 1xN and 2xN sub-blocks of ISP
[6] JVET-O0341-V1 Unification of intra interpolation filter selection
[7] JVET-O0502-V3 Proposed ISP cleanup
Tool documents of CST:
[8] JVET-N0137-V5 Chroma separate tree (CST)[9] JVET-N0137-R1 Introduction of CST[10] JVET-N0137-WD-CE3 Algorithm description of CST
Others :
[11] JVET-K0049-V2 Line-based intra coding mode
[12] Li, Jiahao et al. “Efficient Multiple-Line-Based Intra Prediction for HEVC.” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 28.4 (2018): 947–957. Crossref. Web.
[13] JEVT-L0023 CE3: Summary Report on Intra Prediction and Mode Coding
[14] JEVT-L1023 Description of Core Experiment 3 (CE3): Intra Prediction and Mode Coding
[15] JEVT-L0319 CE4-related: Sub-block MV clipping in planar motion vector prediction
[16] JEVT-L0131 Harmonization of Linear interpolation intra prediction (LIP) with Simplified position dependent intra prediction combination (PDPC) and wide-angle intra prediction (WAIP)
[17]
JJEVT-L0283[18] JEVT-M0485 Sub-block MV clip in planar motion vector prediction
[19] Information and Complexity, textbook of “Introduction of Info theory” in 108-1, NTU, Professor H.T. Lin